Webb.ai today opened an early access program access to a Continuous Automated Root Cause Analysis platform that uses artificial intelligence (AI) combined with a knowledge graph to dynamically keep track of and analyze changes to IT environments.
Manish Gupta, CEO of Webb.ai, said the platform uses a mix of machine learning algorithms and generative AI capabilities based on large language models (LLMs) to aggregate alerts into higher-order insights that are presented in natural language to members of a DevOps team.
That approach differs from legacy approaches because it tracks causal relationships between changes versus relying on probabilistic models that tend to create a lot of false positives, he noted.
Webb.ai is also taking advantage of Kubernetes clusters to enable its platform to scale up and down as needed when analyzing data, added Gupta. That platform is also more efficient than other approaches to observability that require IT teams to store massive amounts of data. In contrast, the Continuous Automated Root Cause Analysis automatically surfaces anomalous events that DevOps teams can choose to save rather than requiring them to save all the metrics, logs and traces that would otherwise need to be tracked, he noted.
Most IT incidents can be traced back to the most recent changes made to an IT environment. The challenge is as IT environments have become more complex, it’s not feasible for humans to keep track of those changes without relying on AI and a knowledge graph, said Gupta.
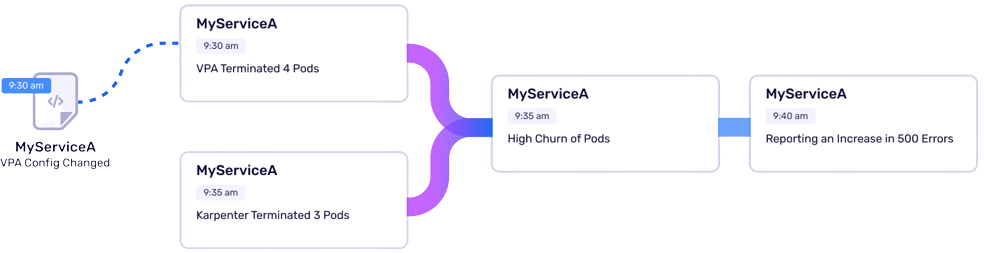
As businesses become more dependent on software to drive digital processes, the cost of downtime is exponentially increasing. The need to identify the root cause of an IT incident as fast as possible has become a critical requirement, he added.
Webb.ai doesn’t see AI technologies replacing the need for DevOps professionals and site reliability engineers (SREs) for at least another 10 to 15 years. In the meantime, many tasks that today are completed manually will be increasingly automated, said Gupta. A DevOps engineer dragged out of bed at 2:00 A.M. to address an issue does not want to have to sift through alerts. Instead, generative AI tools will summarize the issue at hand with recommendations on resolving it, noted Gupta. In effect, DevOps teams will be augmented by AI so they can manage IT environments at even higher levels of scale, he said.
There is always going to be some sense of fear and loathing when it comes to AI, but ultimately, AI should reduce the burnout rates that today adversely affects any organization’s ability to retain DevOps professionals. Far too much time is spent trying to identify the root cause of a slowdown in a cloud-native application’s performance that could be caused by any number of issues involving one dependency or another. The frustrating thing, of course, is that while it may take days to identify the root cause of an issue, it often takes just a few minutes to resolve.





